What is the productivity paradox?
The productivity paradox refers to the observed phenomenon where advancements in information technology (IT) don’t correlate with increased productivity in organizations or economies as expected.

Table of contents
- What is the productivity paradox?
- Why is the productivity paradox important to address?
- Use cases for tackling the productivity paradox
- Using DAPs to overcome the productivity paradox
- Success stories: Overcoming the productivity paradox
- Big brands overcoming the productivity paradox
- Recognizing the signs of a productivity paradox
- Advantages of overcoming a productivity paradox
- Challenges of not overcoming a productivity paradox
- Overcoming the productivity paradox: A game-changer for organizational dynamics
Despite significant investments in IT infrastructure, such as computers, software, and networks, the anticipated productivity, efficiency, and economic growth improvements may not materialize immediately or to the extent predicted.

Several factors contribute to this paradox:
- Lag time: It takes time for organizations to fully integrate new technologies into their workflows and realize productivity gains.
- Measurement challenges: Traditional metrics may not capture the full impact of IT investments on productivity, leading to underestimation of their benefits.
- Organizational and managerial issues: The effective utilization of IT requires changes in organizational structure, work processes, and management practices. Resistance to change or ineffective implementation strategies can hinder productivity improvements.
- Mismatched expectations: Sometimes, the expectations surrounding the potential benefits of IT investments are overly optimistic or unrealistic, leading to disappointment when the anticipated gains are not immediately realized.
- Complexity and unintended consequences: IT systems can introduce new complexities and challenges that offset some expected productivity gains. For example, issues such as information overload, security concerns, and increased demands for skill training can arise. That’s why Gartner has predicted that self-supervised learning will significantly impact existing products and markets.
While the productivity paradox doesn’t negate the long-term benefits of IT investments, it highlights the need for careful planning, effective implementation strategies, and ongoing evaluation to ensure that organizations can maximize the potential benefits of technology.
Why is the productivity paradox important to address?

Overcoming the productivity paradox is essential for organizational success. Gartner states that organizations will need to overcome the productivity slowdown to achieve scalable results from costly digital initiatives.
Businesses should care about overcoming the productivity paradox for several reasons:
Competitive advantage: In competitive markets, businesses that can effectively harness technology to boost productivity gain a significant edge over their rivals. Overcoming the productivity paradox allows enterprises to streamline operations, reduce costs, and deliver products or services more efficiently, enhancing their competitiveness in the market. WalkMe’s State of Digital Adoption 2024 report states that 93% of enterprises need to improve productivity in the next year to remain on par with competitors.
Profitability: Improved productivity often leads to higher profitability. By overcoming the productivity paradox, businesses can achieve higher output with the same or fewer resources, thereby increasing their profit margins. Recent findings from WalkMe indicate that lost productivity costs enterprises $1.14 million every week, highlighting the importance of flipping this trend.
Innovation: Addressing the productivity paradox often requires processes, systems, and technology innovation. Businesses that innovate to overcome productivity challenges are better positioned to adapt to changing market conditions, meet customer needs, and stay ahead of competitors.
Employee satisfaction and retention: WalkMe states that the productivity paradox has already become unmanageable for many enterprises.
For example, 40% of employees resent how hard it is to use corporate technology. They spend vast amounts of time compensating for poor technology experiences, including extra time on tasks because they can’t use their software efficiently or have to ask colleagues or search for help online.
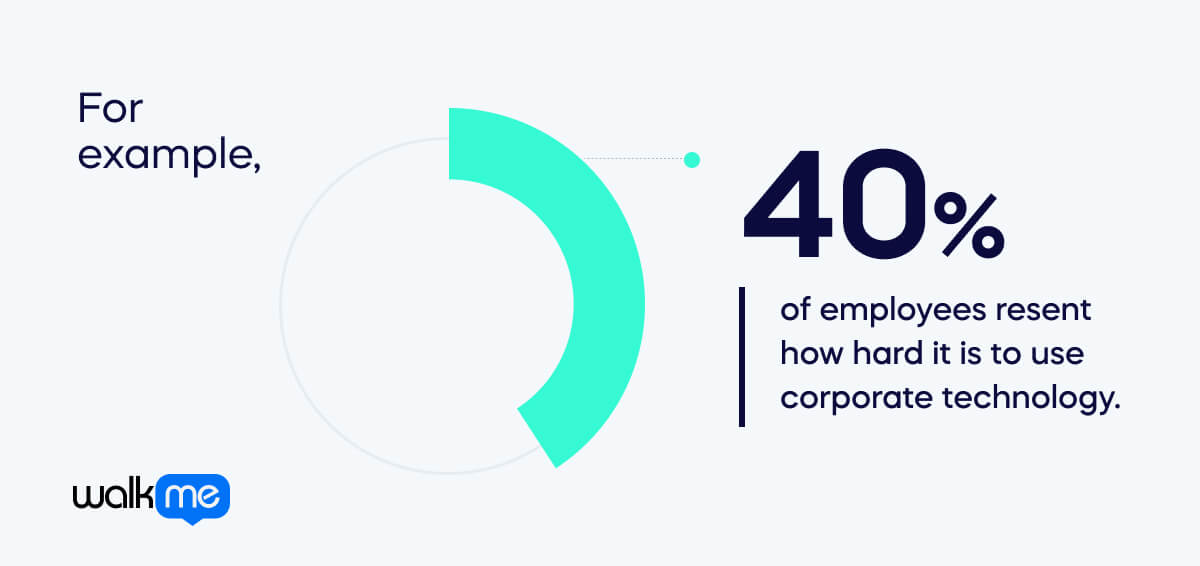
The report states that this amounts to more than 350 hours of yearly lost productivity per employee, or $10,000 annually.
Increased productivity can lead to a more efficient and less stressful work environment. Employees may feel more satisfied when their efforts result in tangible outcomes, leading to higher morale and reduced turnover.
Scalability: Overcoming the productivity paradox allows businesses to scale their operations more effectively. Whether expanding into new markets or handling increased demand, improved productivity enables companies to grow without proportionally increasing costs.
Resource optimization: By identifying and addressing inefficiencies, businesses can optimize the allocation of resources such as time, capital, and human resources. This ensures that resources are utilized effectively, minimizing waste and maximizing returns.
WalkMe, as a leading digital adoption platform, plays a pivotal role in addressing the productivity paradox. Let’s explore how:
Technology overwhelm: The proliferation of digital tools, platforms, and apps can overwhelm employees. WalkMe reveals that the leading causes of hindered organizational efficiency and employee performance include a lack of knowledge about available resources and inadequate support structures.
While technology offers tremendous value, it can also be a distraction if not harnessed effectively. The report also states that:
- 16% of working days a year are spent by employees compensating for lack of application proficiency
- 32% of employees regularly have to work late because of hard-to-use technology
- 31% of employees have missed or had mistakes with at least one day of holiday or sick leave in the past year because of hard-to-use HR systems
WalkMe helps by providing contextual guidance, simplifying complex processes, and ensuring users maximize the potential of various tools.
End-user adoption: Many organizations struggle with end-user adoption despite substantial software investments. Outdated change management programs hinder successful digital transformation projects. WalkMe bridges this gap by offering personalized, step-by-step guidance, ensuring users embrace new technologies seamlessly.
Data-driven decision-making: WalkMe enables data-driven insights. Organizations can identify bottlenecks, optimize workflows, and enhance productivity by analyzing user interactions. Real-time data empowers leaders to make informed decisions, driving efficiency and effectiveness.
Here are some ways WalkMe directly impacts productivity:
- Onboarding and training: WalkMe simplifies onboarding for new employees. Interactive walkthroughs guide them through software interfaces, reducing the learning curve and accelerating productivity.
- Process automation: WalkMe automates repetitive tasks, freeing up employees’ time. Streamlining processes enhances efficiency and allows staff to focus on value-added activities.
- User experience enhancement: WalkMe ensures a seamless user experience by providing in-app assistance. Whether completing forms, navigating complex workflows, or troubleshooting, WalkMe guides users, minimizing frustration and maximizing productivity.
Use cases for tackling the productivity paradox
Let’s delve into practical scenarios where the productivity paradox is actively addressed:
Strategic alignment and employee empowerment:
In this scenario, a company invests in technology to have the latest tools and align its IT strategy with its overall business objectives.
Moreover, the company empowers its employees by providing them with the necessary training and resources to make the most out of these technologies.
By ensuring that technology adoption is strategic and that employees are equipped to leverage it effectively, the company can overcome the productivity paradox and see real improvements in efficiency and output.
Continuous improvement and agile practices: Companies that embrace continuous improvement methodologies such as Agile and Lean are often better positioned to overcome the productivity paradox. These approaches emphasize iterative development, frequent feedback loops, and a focus on delivering value to the customer.
By breaking down projects into smaller, manageable chunks and regularly reassessing priorities, teams can quickly identify and address inefficiencies in their processes.
This iterative approach to improvement, coupled with the flexibility of Agile practices, allows companies to adapt to changing market conditions and technological advancements more effectively, ultimately driving productivity gains.
Data-driven decision-making: Another way to overcome the productivity paradox is leveraging data to drive decision-making processes.
Companies that invest in robust data analytics tools and practices can gain valuable insights into their operations, customer behavior, and market trends.
By using these insights to inform their strategic planning and day-to-day operations, companies can identify areas for improvement and optimize their processes more effectively.
Additionally, data-driven decision-making can help companies better allocate resources, prioritize projects, and measure performance, leading to increased productivity and competitiveness in the marketplace.
Using DAPs to overcome the productivity paradox
DAPs like WalkMe can help organizations overcome the productivity paradox and significantly improve their bottom line. Here are some examples of ways that WalkMe can help:
Software adoption and training
Scenario: A large organization adopts a new customer relationship management (CRM) software. Despite the investment, employees struggle to use it effectively, leading to productivity losses.
Solution: By implementing WalkMe, the organization provides in-app guidance during onboarding. WalkMe’s interactive walkthroughs help users navigate the CRM system, understand its features, and perform tasks efficiently. As a result, user adoption increases, and productivity improves.
Process optimization
Scenario: A financial institution faces challenges in streamlining loan approval processes. Employees spend excessive time manually reviewing documents and handling paperwork.
Solution: WalkMe identifies bottlenecks by analyzing user interactions within the loan management system. It suggests process improvements, automates repetitive steps, and guides employees through complex workflows. The result is faster loan approvals, reduced administrative burden, and increased productivity.
Employee self-service
Scenario: An HR department receives numerous inquiries related to leave requests, benefits, and payroll. HR staff spend significant time answering routine queries.
Solution: WalkMe integrates with the organization’s intranet or HR portal. It offers self-service options, such as guided forms for leave requests or FAQs. Employees can find answers independently, reducing HR’s workload and allowing them to focus on strategic tasks.
Software updates and changes
Scenario: A software company releases a major update to its project management tool. Users resist the change, leading to productivity dips.
Solution: WalkMe provides contextual guidance during the transition. It highlights new features, explains changes, and assists users in adapting to the updated interface. By minimizing the learning curve, WalkMe ensures a smoother transition and maintains productivity levels.
Healthcare systems
Scenario: Healthcare professionals use electronic health record (EHR) systems for patient management. However, cumbersome interfaces and complex workflows hinder their efficiency.
Solution: WalkMe overlays the EHR system, offering real-time assistance. When doctors or nurses need to input data, prescribe medications, or retrieve patient history, WalkMe guides them step by step. This reduces errors, enhances productivity, and improves patient care.
Customer support and ticketing systems
Scenario: A customer support team handles a high volume of inquiries. Agents struggle to find relevant information quickly, impacting response times.
Solution: WalkMe integrates with the support platform. WalkMe suggests relevant articles, macros, or procedures when agents search for solutions or escalate tickets. This speeds up issue resolution, improves customer satisfaction, and boosts agent productivity.
Success stories: Overcoming the productivity paradox
DAPs like WalkMe can help companies of all shapes and sizes overcome the productivity paradox. Here are just a few examples:
Sprinklr
Sprinklr, a social media management platform, faced challenges in employee productivity and user engagement.
The company implemented WalkMe to streamline user workflows within its platform.
WalkMe provided in-app guidance, tooltips, and contextual support. The CoE at Sprinklr ensured that employees fully utilized Sprinklr’s features.
Sprinklr reduced support requests by up to 85% by empowering users with self-service guidance.
Employees spent more time actively using Sprinklr’s platform, leading to better productivity.
Sprinklr witnessed a 330% increase in the adoption of critical features.
Nestlé
Nestlé, a global food and beverage company, aimed to improve employee engagement and productivity.
WalkMe guided employees through various technologies, enabling self-service. They also streamlined workflows, helping employees get things done faster.
Nestlé estimated $30 million in productivity gains across 270,000+ team members.
IBM
IBM sought revenue growth and increased adoption of digital offerings.
WalkMe improved product usage by providing real-time assistance and ensured seamless interactions with IBM’s digital solutions.
IBM achieved 80% revenue growth in digital offerings.
Big brands overcoming the productivity paradox
Here are some examples of big brands that effectively overcame the productivity paradox through their digital adoption strategies:
Toyota
Toyota implemented a comprehensive digital transformation strategy known as the Toyota Production System (TPS), which focuses on lean manufacturing principles and continuous improvement. TPS integrates digital technologies such as IoT sensors, real-time data analytics, and automation to optimize production processes and eliminate waste.
By digitizing its manufacturing operations, Toyota gained greater visibility and control over its supply chain, enabling Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory management and reducing inventory carrying costs.
Furthermore, Toyota emphasizes employee training and engagement to ensure that workers are proficient in using digital tools and empowered to contribute ideas for process improvement, driving productivity gains at all levels of the organization.
Procter & Gamble (P&G)
P&G embraced digital technologies to streamline its product development and marketing processes. The company implemented collaborative tools and cloud-based platforms to facilitate communication and collaboration among global teams, speeding up decision-making and reducing time-to-market for new products.
P&G also leveraged data analytics and consumer insights to personalize marketing campaigns and optimize product assortments, resulting in higher sales and market share.
Additionally, P&G invested in employee training programs to ensure that staff members had the necessary digital skills to leverage new technologies effectively, fostering a culture of innovation and continuous learning.
Recognizing the signs of a productivity paradox
Recognizing the signs of experiencing a productivity paradox within an organization is crucial for taking corrective actions. Here are some common indicators that may suggest a productivity paradox:
Stagnant or declining productivity growth: Despite significant investments in technology and resources, there is little to no improvement in productivity levels over time. This could indicate that the expected gains from technology adoption are not being realized.
High technology spending with minimal impact: The organization allocates a substantial budget to implementing new technologies, yet there is limited evidence of tangible benefits or returns on investment regarding productivity improvements or cost savings.
Increased complexity and overhead: Rather than streamlining operations, introducing new technologies has increased complexity, bureaucracy, or overhead costs. Processes may have become more convoluted, resulting in inefficiencies and reduced productivity.
Resistance or low adoption rates: Employees resist using new technologies or fail to fully embrace them in their day-to-day work. Low adoption rates indicate that the technology solutions implemented do not effectively address the needs or challenges of the workforce.
Poor integration and interoperability: Disparate systems and technologies within the organization may hinder seamless data exchange and collaboration across departments or functions. This lack of integration can lead to duplicated efforts, data silos, and inefficiencies.
Lack of alignment with business objectives: Technology initiatives are not closely aligned with the organization’s strategic goals and priorities. As a result, there may be a disconnect between the investments made in technology and the desired outcomes in terms of productivity, profitability, or customer satisfaction.
Unsatisfactory customer experience: Despite technological advancements, customers may experience delays, errors, or inconsistencies in service delivery or product quality. This may indicate underlying inefficiencies in the organization’s processes or operations.
Employee burnout and disengagement: Increased reliance on technology without proper support or training can lead to burnout or disengagement. Overwhelmed by complex systems or automation, employees may experience heightened stress levels and reduced job satisfaction, ultimately impacting productivity.
Ineffective use of data and analytics: Despite collecting vast amounts of data, the organization struggles to derive meaningful insights or actionable intelligence. This may indicate a lack of analytical capabilities or a failure to translate data into informed decision-making and process improvements.
Lack of continuous improvement culture: The organization lacks a culture of continuous improvement and innovation, where employees are encouraged to identify and address inefficiencies proactively. Without a focus on ongoing optimization, productivity gains may plateau or decline over time.
Advantages of overcoming a productivity paradox
Overcoming a productivity paradox can yield several significant advantages for organizations, including:
Increased efficiency: Organizations can achieve higher productivity levels with the same or fewer resources by resolving inefficiencies and streamlining processes. This allows for more efficient utilization of labor, capital, and other inputs, leading to cost savings and improved profitability.
Competitive advantage: Enhanced productivity enables organizations to deliver products or services more quickly, reliably, and cost-effectively than their competitors. This can lead to a stronger market position, increased market share, and greater customer satisfaction, ultimately driving sustainable competitive advantage.
Innovation and growth: By freeing up resources and capacity through improved productivity, organizations can allocate more resources to innovation and strategic initiatives. This fosters a culture of creativity and experimentation, leading to new products, services, and business models that drive future growth and differentiation.
Adaptability to change: Agile and productive organizations are better equipped to adapt to changing market conditions, technological advancements, and competitive pressures. They can quickly pivot their operations, respond to customer needs, and capitalize on emerging opportunities, mitigating risks and maintaining relevance in dynamic environments.
Employee engagement and satisfaction: Increased productivity can lead to a more fulfilling and rewarding work experience for employees. When employees see their efforts translating into tangible results and success for the organization, they are more motivated, engaged, and satisfied in their roles, leading to higher morale, retention, and performance.
Better customer experience: Improved productivity enables organizations to deliver a higher quality of products or services, faster response times, and more personalized customer experiences. This enhances customer satisfaction, loyalty, and advocacy, driving repeat business and positive word-of-mouth referrals.
Financial performance: Overcoming the productivity paradox can directly impact an organization’s economic performance. Increased productivity translates into higher revenues, lower costs, improved margins, and greater profitability and shareholder value.
Sustainability and resilience: Productive organizations are better positioned to weather economic downturns, market disruptions, and other challenges. By operating efficiently and effectively, they can maintain stability, preserve resources, and sustain operations during periods of uncertainty, ensuring long-term viability and resilience.
Challenges of not overcoming a productivity paradox
Failing to overcome a productivity paradox can pose several challenges and risks for organizations, including:
Wasted resources: Organizations may continue to invest significant resources in technology and process improvements without realizing the expected productivity gains. This wastes time, money, and effort, diverting valuable resources away from more productive uses.
Stagnant growth: Without productivity improvements, organizations may struggle to achieve sustainable growth and profitability. This can limit opportunities for expansion into new markets, product lines, or customer segments, constraining the organization’s ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities and trends.
Operational inefficiencies: Productivity paradoxes often result in inefficiencies and bottlenecks within organizational processes. This can lead to delays, errors, and inconsistencies in product delivery or service quality, eroding customer satisfaction and loyalty over time.
Employee frustration and burnout: Employees may become frustrated and demoralized when they perceive their efforts not translating into meaningful productivity improvements. This can lead to increased stress, burnout, and turnover, impacting morale, engagement, and organizational performance.
Missed innovation opportunities: Organizations preoccupied with addressing productivity challenges may neglect investments in innovation and strategic initiatives. This stifles creativity and hinders the development of new products, services, and business models essential for long-term growth and competitiveness.
Financial strain: Persistent productivity paradoxes can strain the organization’s financial resources and performance. Increased costs, lower revenues, and reduced profitability may lead to financial instability, cash flow problems, and difficulty securing investment or financing for future initiatives.
Risk of obsolescence: Organizations that fail to adapt and evolve in response to changing market dynamics and technological advancements risk becoming obsolete. They may lose relevance in their industry and struggle to attract customers, talent, or investment, ultimately facing decline or even failure in the long term.
Overcoming the productivity paradox: A game-changer for organizational dynamics
Overcoming the productivity paradox can significantly reshape organizational dynamics:
Cultural transformation
The paradox often arises from a disconnect between technology adoption and actual productivity gains.
Organizations must foster a culture that prioritizes productivity over mere technology adoption. This shift involves aligning leadership, teams, and processes toward a common efficiency goal.
Agility and adaptability
Organizations sometimes struggle to adapt quickly to technological changes.
Overcoming the paradox requires agility. Teams must embrace change, experiment with new tools, and continuously learn. An adaptable workforce ensures smoother transitions during technology adoption.
Collaboration and communication
Technology can inadvertently isolate employees if not implemented thoughtfully.
Effective digital adoption fosters collaboration. When employees engage with technology seamlessly, they collaborate better across departments. Clear communication channels become essential for sharing best practices and insights.
User-centric approach
Technology adoption often focuses on features rather than user needs.
Prioritizing user experience is critical. Digital Adoption Platforms (DAPs) like WalkMe provide in-app guidance, ensuring employees fully embrace technology. When users find tools intuitive and helpful, they engage more effectively.
Data-driven decision-making
Lack of data-driven insights hinders productivity improvements.
DAPs offer analytics to track feature usage, identify bottlenecks, and optimize processes. Informed decisions based on data lead to better productivity outcomes.
Empowering employees
Disengaged employees contribute to the paradox.
When employees feel empowered by technology, they become more productive. DAPs simplify workflows, reduce the learning curve, and enhance self-service capabilities.