The AI landscape changed forever when the business world saw the release of the generative AI tool ChatGPT in November 2022.
However, not every change is good and can be challenging to measure if you don’t know what artificial intelligence tools your staff are using.
Managing unauthorized AI tool usage via open communication and a transparent shadow IT AI policy can reduce risk and promote a healthy corporate culture.
96% of security professionals admit to someone at their organization using unauthorized AI tools. This suggests that many staff members, especially those without a security background, might also be using such unapproved tools, potentially unaware of the associated risks.

To help you understand the process of managing unauthorized AI tool usage, we will explore the following topics:
- What is unauthorized AI tool usage?
- Why unauthorized AI tool usage happens
- The risks of not managing unauthorized AI tool usage
- How to manage unauthorized AI tool usage

Unauthorized AI tool usage is when staff use AI tools, like ChatGPT or Google Bard when such tools are not on their IT department’s approved tools list.
Although this activity carries various risks along with some benefits, it’s important for staff to openly communicate about the tools they are using.
Simultaneously, organizations should understand the reasons behind staff members’ choice of these tools, as this understanding can help in curbing unauthorized usage.
Employees often use unauthorized AI tools to fulfill particular requirements or promptly tackle challenges. Organizations must confront this practice as it has the potential to lead to security breaches.
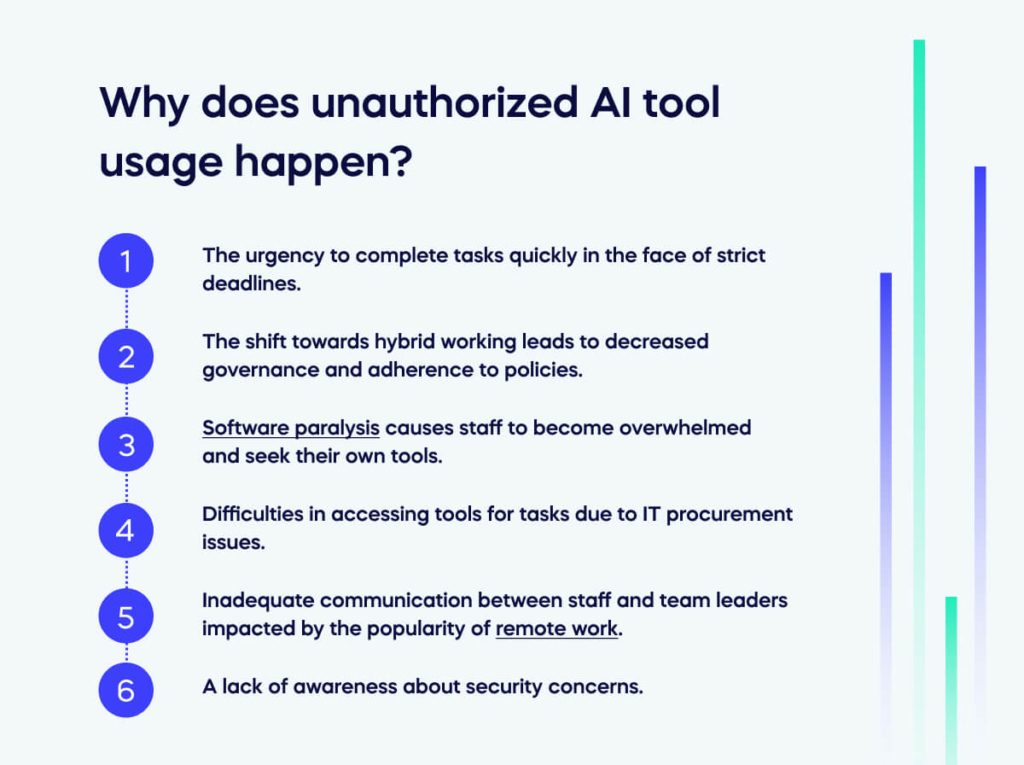
AI tool usage involves various factors, such as:
- The urgency to complete tasks quickly in the face of strict deadlines.
- The shift towards hybrid working leads to decreased governance and adherence to policies.
- Software paralysis causes staff to become overwhelmed and seek their own tools.
- Difficulties in accessing tools for tasks due to IT procurement issues.
- Inadequate communication between staff and team leaders impacted by the popularity of remote work.
- A lack of awareness about security concerns.
Awareness of these reasons is the key to understanding why your staff use these tools and can aid communication as you try to deal with unsanctioned usage.
Also, be aware that the above reasons are the most common, but only by asking your staff can you learn their reasons for using unauthorized apps within your organization.
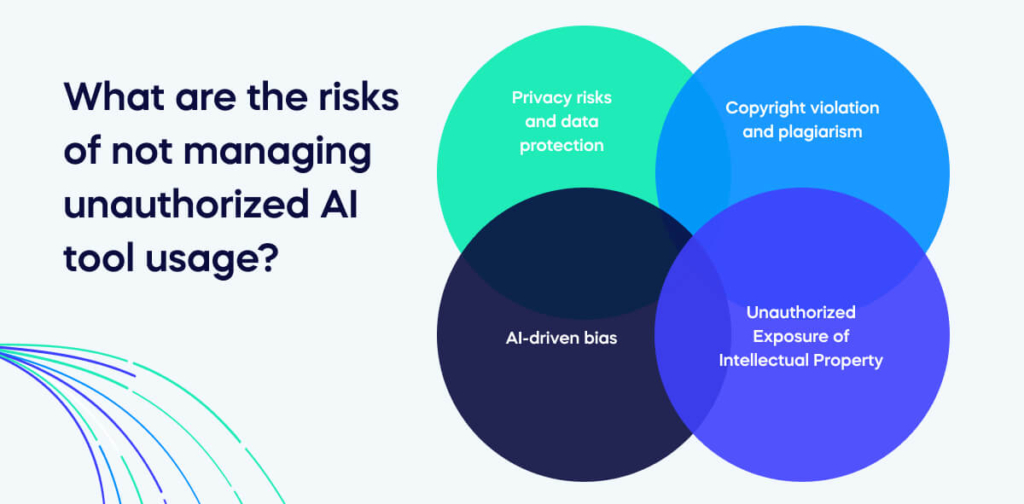
The four main risks of not managing your staff’s use of AI tools not included on the IT authorized list are often large in the scale of how they can negatively impact your organization, from security breaches of confidential data to damage to your brand.
1. Privacy risks and data protection

AI tools present a substantial threat to data and privacy security and show how data security risks like breaches staff can avoid when using authorized AI tools.
Uploading sensitive information to generative AI tools can result in breaches of privacy and trust, potentially causing financial losses and harm to the company’s reputation.
Generative AI models without human oversight are susceptible to data poisoning, directing users to imposter websites housing ransomware.
After all, it is useless to encrypt data if your staff are entering it into unauthorized AI tools without knowing how the tool will use it.
Using AI tools improperly can lead to vast amounts of data getting into the wrong hands. This scenario happened recently when Microsoft AI researchers leaked 38TB (38 hard drives worth) of confidential data.
Established multinationals like Microsoft can recover quickly from the temporary damage to their brand. Still, smaller companies should avoid security breaches as they may not recover so soon or at all.
2. Copyright violation and plagiarism
While AI technology excels at rapid content generation, it fails to produce unique or flawless text.
Employing AI-generated content without manual editing poses the danger of creating duplicative content, potentially viewed as plagiarism.
Additionally, AI tools can inadvertently expose a business to copyright infringement issues related to the intellectual property of other businesses.

Many enterprises face challenges because AI companies like OpenAI face legal challenges due to using content with contested permission.
Laws in this area are changing, so continuously update your knowledge and disseminate this to staff to ensure they know the dangers of using AI tools facing legal challenges.
3. Unauthorized Exposure of Intellectual Property
Unchecked employee utilization of generative AI may result in unintentional unauthorized disclosure of intellectual property, confidential information, and trade secrets.
Companies lacking policies and procedures to govern the workplace use of generative AI are susceptible to potentially losing valuable assets.
Ensure your staff knows the basics of measures to avoid unauthorized exposure of your organization’s intellectual property to avoid the sensitive data you work so hard to secure getting into the hands of the public or your competitors.
4. AI-driven bias
AI bias in the way it treats sex, disabilities, or other personal factors poses a significant risk to corporations as it can lead to unfair treatment, damaged reputation, and legal consequences.
One of the best-known examples occurred when Amazon faced backlash when its AI hiring tool exhibited gender bias, favoring male candidates.

This incident highlighted the urgent need for corporations to address and rectify biases in AI systems to ensure fairness, diversity, and ethical use.
Train your staff on bias to ensure they are mindful when choosing an AI tool, especially in recruitment, where it could have unintended consequences.
A crucial element of encouraging staff to avoid unapproved AI apps involves crafting a suitable governance framework.
Each institution should evaluate its specific AI applications, risk profile, and risk tolerance via thorough data analysis, tailoring governance frameworks to its unique circumstances.

Consider the tactical steps below to manage compliance risk as AI integrates into your processes.
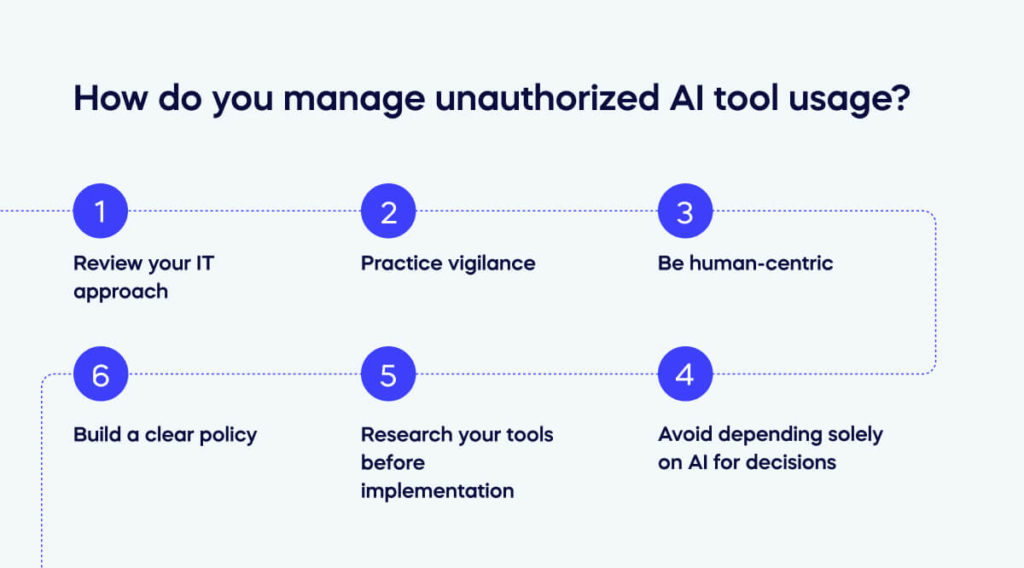
Review your IT approach
Recognize the nuances in financial institutions where AI falls short of replacing humans, particularly in tasks demanding nuanced judgment and contextual understanding. Address these limitations to ensure responsible and effective AI integration within the organization.
Practice vigilance
Maintain a vigilant stance on potential risks associated with poor data quality, machine learning challenges, and the looming threats of AI attacks. Uphold organizational integrity by proactively addressing and mitigating these risks.
Be human-centric
Embrace a human-centric approach to AI management, integrating manual reviews to defend against discriminatory AI tendencies. This approach ensures ethical and fair AI applications, fostering a culture of inclusivity and responsibility within the organization.
Avoid depending solely on AI for decisions
Acknowledge the substantial impact algorithms can have on decision-making processes, emphasizing the need for careful consideration and continuous monitoring to avoid unintended consequences and uphold the integrity of organizational decisions.
Research your tools before implementation
Prioritize a thorough vetting process for AI applications before widespread adoption.
Keep a close eye on digital asset identity for existing tools and mitigate risks of reputational damage by ensuring alignment with organizational values, ethical standards, and overall goals despite potential gains in productivity and cost savings.
Build a clear policy
Establish a comprehensive AI tool usage policy, emphasizing the inclusion of employee feedback at every stage of development and implementation. This collaborative approach ensures a well-rounded, effective, and ethically sound framework for AI integration.
Following these strategies will help you manage your team’s unauthorized usage of AI tools by listening to their needs and making them aware of the reasons for using only authorized apps.
This approach will lead to long-term success, as staff will be happier with the policy formed partly from their feedback and understand the reasons for its implementation.
Reduce AI usage risks with education and support
Educating and supporting users about the risks associated with unauthorized AI usage is crucial in minimizing potential threats.
By providing comprehensive training on AI ethics, security protocols, and responsible utilization and training on why only authorized personnel have access to certain data, your organization can empower your workforce to make informed decisions.
This proactive approach safeguards against unintended consequences and fosters a culture of responsible AI use through excellent employee experience within any organization, guiding you to success.


