Driving organizational success hinges on improving and enhancing IT processes.
Companies pursue digital transformation to make IT processes more efficient and productive. In turn, this boosts their financial performance. Such IT process tools also increase organizational agility, adaptability, and competitiveness.
However, the success of any IT process adoption depends on employees using these tools in their daily roles. Poor process adoption can result from various factors. These include unsuccessful implementation, stakeholder misunderstanding, poor design, and lack of support.
Thus, IT process adoption is about more than acquiring the latest technology for your team. It requires consideration of the technology’s suitability for your IT team. This ensures that the chosen technology aligns well with their needs and capabilities.
This article highlights 11 ways to start and sustain IT adoption efforts. It also defines IT process adoption. It also examines the adoption process stages and explains why it is important.
What is IT process adoption?
Adopting IT process involves integrating new technology into your IT infrastructure to enhance processes. Adoption goes beyond using technology. It occurs when your employees fully leverage new technology. This maximizes the tool’s potential and reaps the new system’s benefits.
For instance, a company aiming to streamline its handling of simple support queries may purchase an automated IT AI bot to answer basic process questions. Initially, one or two IT team members might start using this new system.
However, some IT employees may use it differently without proper guidance or support, and others might stick to manual, ad hoc systems. While some employees use the tool in this scenario, they haven’t fully adopted it.
Instead, IT process adoption requires a systematic approach to technology implementation.
11 Ways to achieve successful IT process adoption
If IT users fail to embrace and integrate new technology, the investment wastes money, effort, and time, resulting in a plummeting ROI.
Training users on the new technology alone does not ensure IT process adoption. It also requires securing their buy-in and commitment. Introducing new technology disrupts users’ daily routines, leading to frustration and resistance.
Here are 11 strategies to enhance the likelihood of successful IT process adoption:
- Address the ‘why’ of your IT process issue
To address problems effectively, organizations must first understand their current IT operations. This foundational step is critical for setting the stage for improvement.
The next step involves defining an ‘ideal situation statement.’ This is a concise description of the IT team’s desired future state.
Organizations can pinpoint the discrepancies between the two by documenting the current and desired future. This helps determine the ‘why’ for improving current IT processes.
- Get management on board
Securing the support of the entire IT management team is essential for a successful IT process change. There might be a lack of clear understanding of current issues.
So, explaining the present situation and what you aim to achieve with the change is important. Demonstrating how the change will make a difference can clarify the vision for IT leadership.
Gaining executive buy-in hinges on highlighting the advantages of the IT process change. You must show that the change is not just for short-term fixes but addresses deeper needs, offering long-lasting benefits.
Make a compelling case by linking the change to tangible outcomes. These include improved profitability, enhanced competitiveness, entry into new markets, or accelerated growth.
If the IT management team understands the purpose of the process change and is on board, they can also help IT support staff on board.
- Align the new IT process tool with your business objectives and goals
When selecting technology for your business, consider more than the vendor’s name and price. Evaluate your strategy and how the new technology will support your strategic objectives.
The goal behind integrating new technology into a business is to enhance performance. Identify your desired outcomes first. Then, work backward to select the technology that best enables performance improvements.
People will be more likely to adopt new technology if it contributes to their goals and objectives. Review your existing technology systems before deploying something new.
Beyond gathering detailed requirements for the new technology, ensure your current systems can support and integrate effectively. Doing this work in advance will avoid system overlaps, reduce build times, and keep your budget in check.
- Develop a change management plan to support deployment
Prioritizing a change management plan is crucial for any IT process change, whether digital, physical, or cultural. From the outset, involving stakeholders in implementing, redesigning, or replacing processes ensures transparency.
This leads to higher quality and more timely feedback for making necessary adjustments. Establishing change management procedures is essential for enabling all current and future employees or stakeholders to adopt new IT processes effectively.
Leveraging a digital adoption platform can help organizations develop comprehensive onboarding, training, and support processes. Features like push notifications, smart launchers, and tooltips embedded within a tool offer real-time guidance to IT users exactly when needed.
- Take the view of the IT support team into account
Resolving support requests can take hours to days.
Given the volume and complexity of support inquiries, these teams can quickly become overwhelmed, leading to a pile-up of tasks. A new IT support process could be considered a new self-service support tool.
Self-service support enables users to independently consult a knowledge base to address minor support issues.
Having documentation readily available when needed can boost productivity, reduce support expenses, lessen the number of support requests, and alleviate the burden on the support team.
However, for effective integration, the IT support team must understand the practical application of self-service support within their current processes.
Failing to notify your support team about transitioning to a new process tool can lead to issues. Including the IT support team in the decision-making process for new software implementation is crucial.
Their expertise in the company’s existing systems and the new software’s compatibility with those systems is invaluable.
Additionally, it is necessary to secure the IT support department’s support early. They will oversee the software’s implementation. You must consider their schedule and priorities during the adoption phase of the new IT process.
- Communicate expectations and changes at the onset
Making your IT process adoption successful hinges on effective communication. This means establishing a robust communication plan before the tool’s introduction.
This approach could include organizing town hall meetings to explain the reasons behind the changes. It will also give employees a chance to have their questions addressed.
You could also develop FAQ sheets or informational one-pagers and distribute them to your IT team.
Remember, communication is a two-way street. It’s not enough to just inform your employees about the changes. You need to engage them in the process.
Encouraging their feedback is crucial for securing their buy-in. It also helps them feel part of the decision-making process.
This employee engagement helps address concerns about the new software before its implementation.
Moreover, pay attention to your language when discussing the new software. Opt for clear, straightforward language that highlights the software’s benefits. This can include how it will streamline their tasks or simplify their processes.
- Champion and incentivize early adopters
Identify your IT innovators and early adopters and empower them to lead the adoption of this new software among your other users. Innovators and early adopters typically show the most enthusiasm for new software in your organization.
They are more likely to incorporate the new software into their daily routines. They will also use their excitement to motivate even the most hesitant employees to try it out.
Make sure your champions fully understand why you chose this particular software. Share with them the reasoning behind your decision.
You should highlight how you compared it with other market options. This will make it easier to relay this information during discussions with fellow IT employees.
Consider offering incentives to early adopters to highlight the importance of these new systems. These incentives might be financial rewards such as bonuses and salary hikes or opportunities for professional development and networking. You might also offer work flexibility options, paid time off, or dedicated days for mental health.
- Consider a variety of training methods to aid IT process adoption
A significant barrier to user adoption is inadequate and tailored training. While many vendors include training with the purchase of new technology, such training often comes in a one-size-fits-all format. It lacks customization for specific business processes or organizational culture.
Effective employee training goes beyond mere screenshots and presentations. Before the system officially launches, IT employees need hands-on experience with it within the context of their own work processes.
Providing irrelevant or generic training can lead to increased resistance and reduced adoption. This is especially true if stakeholders find the training unhelpful and fail to connect it with their daily tasks.
Furthermore, it is important to recognize that individuals adapt to and learn new technology differently. You can help ensure that all users feel prepared and supported through various training approaches. These include digital resources, traditional classroom settings, and smaller, practical training sessions.
- Take an incremental approach to implementation
Organizations often attempt to digitize all operations simultaneously. The secret to achieving successful IT process adoption lies in taking incremental steps.
When introducing a new IT process tool, it’s best to implement it slowly, focusing on one step at a time after selecting the technology. This approach allows IT staff to adjust at their own pace. This then facilitates the seamless incorporation of the technology into their daily routines.
Starting with a pilot project is an effective strategy for adopting a new process tool. It enables the selection of specific individuals and processes for the initial implementation. Then, use the results to determine the most effective strategy for broader deployment across the team.
- Celebrate wins and progress often
Change can be disconcerting for most people. Motivating and affirming your employees is crucial throughout the entire IT process implementation.
Enable IT staff to achieve small victories to help them embrace new technology quickly. You can set measurable, specific, and achievable adoption goals.
It’s also vital to acknowledge that cultural shifts play a significant role in integrating new technologies within the IT team. Highlighting relevant success stories and promoting the new IT process tool is important for fostering acceptance.
- Monitor and improve your approach continuously
Rolling out new process technology within the IT team can significantly disrupt existing workflows. It’s crucial to track your deployment. Consider breaking the implementation schedule into smaller, more digestible phases if necessary.
Inviting feedback from IT stakeholders is essential, as new technology affects everyone. Listening to their feedback and adjusting your implementation strategy is key to successful adoption.
Creating an employee feedback loop involves everyone in the change process. It also provides valuable insights into the technology’s effectiveness and areas requiring adjustments. Every aspect of the deployment must be measurable and observable.
Don’t assume the new IT process system will operate smoothly without oversight once the implementation begins. Establish clear success and performance metrics. Continuously monitor, assess, and adjust based on these metrics, always focusing on the initial objectives.
What are the stages of IT process adoption?
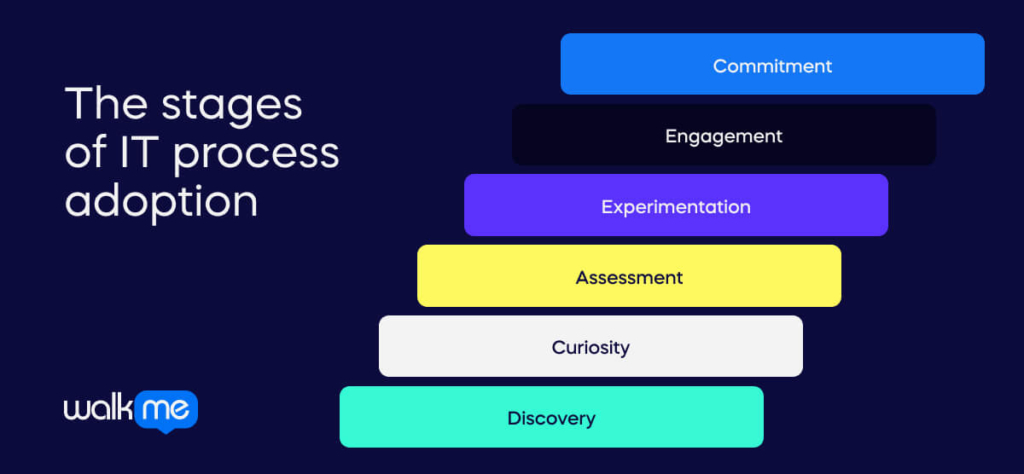
The phases of IT workflow adoption illustrate the different steps employees experience when introduced to a new product or feature.
This differs from the technology adoption curve, which categorizes the type of software users. It also highlights the value of understanding these key user segments to fit your workflow.
At the top of the curve are innovators who want to use new technologies but may not stay long-term.
Early adopters are keen on practical solutions and offer valuable feedback. The early majority prefers risk-free, proven products. The late majority has little patience for technical issues. Laggards resist change, only adapting when necessary.
The stages of IT process adoption include:
- Discovery: Identifying the product through marketing or communication initiatives.
- Curiosity: Gathering more information to assess compatibility.
- Assessment: Analyzing the benefits and drawbacks.
- Experimentation: Trying out the product on a trial basis.
- Engagement: Realizing the product’s worth and interacting with an essential function.
- Commitment: Deciding whether to persist or cease usage.
Why is IT process adoption important?
IT process adoption is important as it can maximize technology use and enhance productivity. It can also improve efficiency, driving better returns on technology investments. Without leveraging technology to refine IT processes, companies risk declining performance. They can also struggle to stay competitive or maintain business continuity.
However, achieving IT process adoption is not easy. Adopting new IT software can challenge employees due to cultural resistance or reluctance to learn new systems. Misalignments between existing processes and new software functionalities may require process overhauls to prevent disruptions.
A lack of leadership support for digital transformation can further hinder adoption. This is often due to unclear objectives or plans for using the technology. As a result, it can lead to frustration and potential abandonment of initiatives.
The absence of necessary skills for adopting new technology can impede progress. This is why you require the adoption strategies for the IT process discussed earlier in this article.
The future of IT process adoption
As technology advances, businesses must adapt to new solutions to remain competitive. However, adopting new IT processes isn’t straightforward. It can disrupt employee routines, necessitate the formation of new habits, and present challenges during implementation.
Familiarity with the technology adoption curve and understanding the nuances of IT process adoption enable businesses to tailor their strategies effectively.
Success in this endeavor involves acknowledging user needs, adopting a long-term perspective, providing targeted training, and maintaining agility. A digital adoption platform (DAP) can be instrumental in this process.
It can offer in-app guidance and support to ensure employees fully embrace digital processes. This then enhances IT process adoption and optimizes technology investment returns.
It can also help evaluate new IT processes to pinpoint areas of user friction and inefficiency. Following this, it can craft optimal user journeys and gauge adoption rates. As a result, seamless IT processes become a reality, driving business growth and a future-proofed technology foundation.


