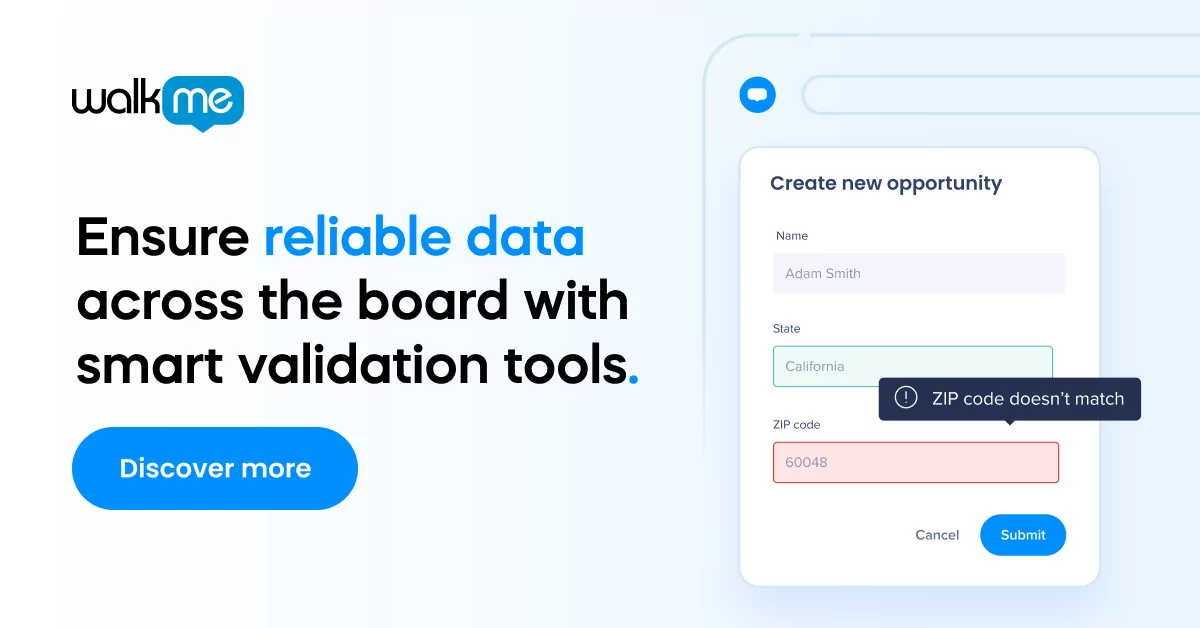
Marked by Gartner as a top tech trend for 2021, total experience is an overarching approach that links disciplines such as the user experience, the customer experience, the employee experience, and multiexperience.
Having a total experience strategy that addresses all of these areas can generate a competitive advantage and help align teams that might otherwise be siloed and pursuing separate agendas.
For the end customer, an effective total experience strategy can drive better interactions, products, services, and more. For the employee, a better experience can improve employee productivity, engagement, and retention, among other key metrics.
All of this, in turn, can improve a company’s reputation, its bottom line, and its relationships with its customers.
Understanding the total experience
A total experience strategy focuses on streamlining, integrating, and aligning a variety of experience functions under a single umbrella.
When executed correctly, total experience creates a seamless world for your employees and customers to inhabit.
Customer experience. The customer experience refers to the sum total of interactions and experiences a customer has with a brand. It is sometimes used synonymously with terms such as “brand experience.”
This discipline extends across a number of fields and business functions, such as customer service, product management, and marketing.
User experience. Like the customer experience, the user experience also focuses on the experience of the end-user. Frequently, however, user experience is a discipline that focuses more on the design of products and a user’s engagement with said products.
Multiexperience. Multiexperience and omnichannel refer to the interactions of customers with the brand across multiple devices, such as mobile phones, desktop computers, and televisions, as well as different mediums, such as social networks and the web.
A solid multiexperience strategy emphasizes the importance of integrating these various channels and technologies into a streamlined and consistent experience.
Employee experience. The employee experience refers to the sum total of interactions employees have throughout their relationship with the company. Factors that affect the employee experience can include everything from the work environment to the corporate culture to workplace software.
Combining these strategies into a single total experience strategy can improve consistency across all channels and for all stakeholders involved. Ultimately, an effectively executed total experience strategy will drive performance improvements and better outcomes across the entire organization.
5 tips for creating a total experience strategy
1. Develop a dedicated business function
First and foremost, it is necessary to formalize a business unit that focuses on the total experience.
One of the best places to start is by creating a cross-functional team that includes all of the relevant experience disciplines mentioned above, including customer experience, employee experience, user experience, as well as other adjacent disciplines that may be unique to your organization, such as product development and UI design.
Once a team has been created, they can set about creating a strategy that focuses on critical tasks such as tearing down silos between business units, branding both the customer and employee experience, and setting overarching strategic goals.
2. Use data to analyze, understand, and improve your strategy
Data should drive all business efforts, including total experience strategies.
In some cases, this may be a challenge in and of itself. Many organizations are still lacking integrated data management strategies.
In such instances, it will be necessary to find ways to combine and view data across the organization and develop more mature data practices. This means not only adopting data tools and technology, but also implementing data-driven methods and even cultivating a data-driven culture.
3. Keep a lookout for current business trends
Pay close attention to trends that are driving the needs and sentiment of customers and employees.
Customer sentiment changes frequently. Technology, major events such as the COVID-19 pandemic, and the passage of time itself can drive changes to customer behavior and demand.
Likewise, employee sentiment can also evolve. COVID-19 and the remote work tidal wave have now driven a demand for hybrid working arrangements, such as flexible working hours and remote work.
These trends should lie at the heart of every total experience strategy, so it is critical to consider such moving parts when making strategic decisions.
4. Reach into the future
To stay ahead of the curve, it is not only important to pay attention to current trends, you must also constantly be forward-thinking.
Digital innovation will give rise to certain predictable trends and technologies, such as augmented reality (AR), the Internet of Things (IoT), and automation in the workplace, to name but a few.
Knowing that these trends are coming can help you plan for their arrival and meet customer demands when they do change.
5. Differentiate yourself from competitors
For many consumers, experience is the key differentiator between brands. All else being equal, that experience can attract or repel a customer from your brand.
For this reason, it is important to develop an experience that is uniquely tailored to the needs and preferences of your customer base.
Team members should therefore use data and feedback to develop in-depth profiles of customers, keep those profiles updated continuously, and use that information to create experiences that suit your audience’s tastes while remaining distinct from those offered by competitors.