Procuring enterprise technology can be a complex process, but it is critical to ensure purchases align with the use cases identified by your organization and meet stakeholders’ expectations.
This requires a well-defined procurement management strategy that factors in the technical requirements, business transformation objectives, and budget constraints.
To develop an effective enterprise technology buying process, conducting a comprehensive needs assessment is essential to determine the core functionalities required for the technology. The IT team, C-Suite, and end-users should all be involved in this approach and can provide valuable insights about the organization’s needs and how the technology will be leveraged.
Once the needs assessment is complete, you can start evaluating vendor management solutions. During this phase, it is important to prioritize functionality over cost, as a solution that doesn’t meet the organization’s needs will ultimately be a waste of resources. It is also essential to thoroughly examine vendors, including reviewing references and conducting site visits, as this can help you identify any potential issues or roadblocks.
When evaluating solutions, consider their scalability and integration capabilities. As the organization grows, so will its technology needs, and it is crucial to select a solution that can evolve with the business.
But this is where a lot of organizations fall short. Determining the vendor’s ability to integrate with existing infrastructure is essential, as this can help streamline implementation and drastically reduce IT costs.
This article will provide step-by-step guidance for organizations when buying enterprise technology. The process outlined below is designed to ensure that the selected vendor can meet the organization’s needs and be integrated into their existing infrastructure.
What is enterprise technology buying?

Let’s start off with a clear definition.
Enterprise technology buying is the process of acquiring and implementing technological solutions and software for businesses, organizations, and corporations.
It involves a comprehensive evaluation of available solutions, identifying the organization’s technical requirements, selecting the most appropriate technology, negotiating contracts, ensuring compliance training with relevant standards, and effectively integrating the solution into the existing technology landscape.
The enterprise technology buying process is complex and necessitates the involvement of multiple stakeholders like IT departments, procurement teams, and business leaders. The decision-making process involves assessing the technical capabilities of available solutions, including functionality, scalability, performance, interoperability, security, and supportability.
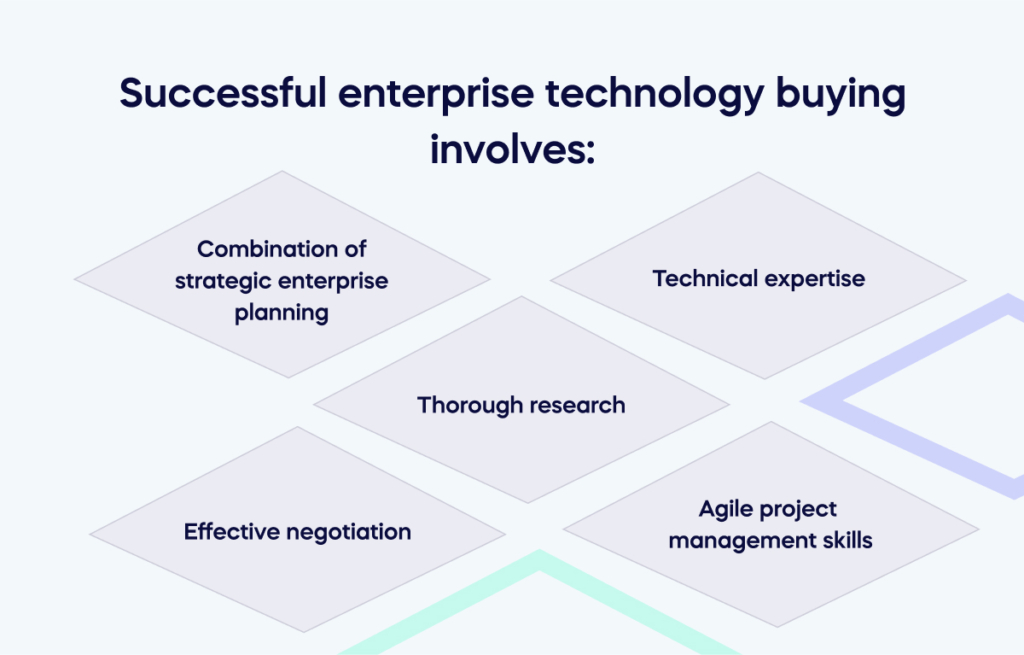
Successful enterprise technology buying involves a combination of strategic enterprise planning, technical expertise, thorough research, effective negotiation, and Agile project management skills to deliver quality solutions that meet the organization’s needs and objectives.
Choosing the right enterprise technology buying method
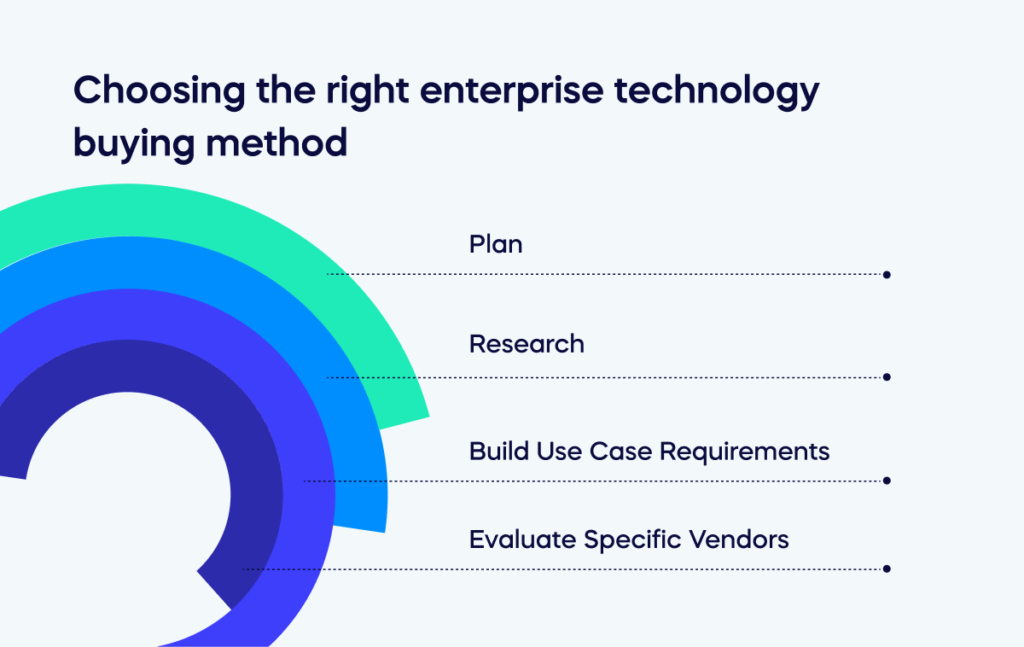
Enterprise tech buyers must follow a rigorous process to successfully evaluate and deploy enterprise technology solutions. This process involves identifying critical stakeholders, aligning objectives, securing a budget, and monitoring progress.
Here are the four key steps in more detail:
Plan
- Create an evaluation team
- Define objectives
- Establish timelines
- Identify budget
- Finalize the plan
Research
- Identify basic needs
- Research technology basics
- Understand the vendor landscape
Build Use Case Requirements
- Identify processes and use cases that the enterprise technology/solutions must support
- Specify detailed requirements and rank them by importance
- Get consensus on those requirements from key stakeholders
Evaluate Specific Vendors
- Share objectives and requirements with vendors
- Evaluate their pitches and proposals
- Conduct detailed due diligence
- Score vendors and make a final choice
Once a vendor is chosen, it’s time to finalize contract parameters and pricing. After awarding a contract, procurement teams or contract specialists should negotiate specific terms. Once the agreement is executed and the vendor is onboarded, the process of getting the purchase to work can begin.
Remember that budgets increasingly come from outside of IT. Therefore, it’s crucial to have a well-defined process in place to ensure that the enterprise technology investment achieves its goals and that the purchasers are satisfied with their decisions.
The 7-step process of enterprise technology buying
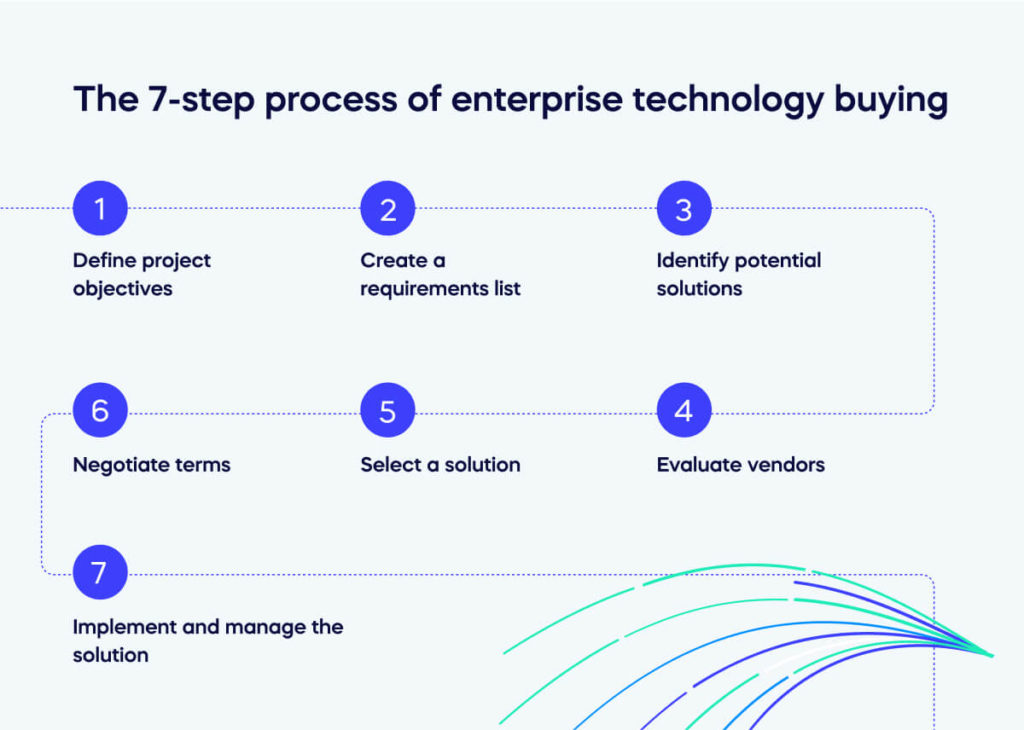
Evaluating and selecting enterprise technologies can be a complex and challenging process.
To help organizations navigate this process, Gartner recommends a 7-step approach that includes defining project objectives, creating a requirements list, identifying potential solutions, evaluating vendors, selecting a solution, negotiating terms, and implementing and managing the solution.
Each step involves careful planning, evaluation, and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure that the technology meets the organization’s needs and achieves its objectives.
Define project objectives
In this step, you should identify the business drivers and define the objectives of the technology purchase. You should determine the expected benefits and outcomes, identify potential risks, and prioritize the needs of stakeholders. It’s important to involve key stakeholders in this step to ensure that the objectives are understood and agreed upon.
You should also consider the impact of the technology purchase on the organization’s existing systems, processes, and culture.
Create a requirements list
This step involves developing a comprehensive list of functional and non-functional requirements that the technology must meet. The requirements should be based on the objectives of the project and should be prioritized based on their importance to the organization.
This includes features, performance, scalability, security, usability, and integration with other systems. It’s important to involve stakeholders in this step to ensure that the requirements reflect the needs of the organization. You should also consider the long-term requirements of the organization to ensure that the solution is scalable and can adapt to changing conditions.
Identify potential solutions
After creating a requirements list, you should research and identify potential solutions that meet those requirements. This can involve reviewing industry reports, attending conferences, and talking to industry experts.
You should create a shortlist of vendors that offer solutions that meet your requirements. This step requires a thorough understanding of the market and the available solutions. You should also evaluate the vendor’s reputation, financial stability, and customer support.
Evaluate vendors
Once you have a shortlist of vendors, you should evaluate them in detail. This step involves conducting demonstrations, interviews, references, and proof of concept to assess the quality of their products, services, and support. You should also evaluate the vendor’s financial viability and ensure they have a track record of successful implementations.
It’s important to involve stakeholders in this step to ensure everyone has input into the decision-making process. You should also consider the vendor’s reputation for innovation, customer support, and service level agreements.
Select a solution
After evaluating the vendors, you should analyze the results and select a solution that best meets your objectives and requirements. This should be a collaborative decision involving all stakeholders.
It’s important to establish clear criteria for selecting the solution and to document the decision-making process. You should also consider the vendor’s ability to integrate with existing systems and processes and their training and support capabilities.
Negotiate terms
Once a vendor has been selected, you should enter into negotiations to finalize pricing, licensing, and service level agreements. This step involves developing a framework for ongoing support and maintenance and establishing clear expectations for deliverables and timelines. Applying legal and procurement teams in this step is important to ensure all agreements are compliant and enforceable.
Consider the vendor’s willingness to be flexible and to work collaboratively with your organization.
Implement and manage the solution
Once terms have been agreed upon, you should work with the vendor to implement the technology and establish ongoing management and support procedures. This includes training employees, establishing processes for reporting issues and receiving support, and monitoring performance against the project’s objectives.
It’s useful to create a governance framework so that the solution stays aligned with the organization’s objectives and strategies. It’s important to involve stakeholders in this step to ensure that the solution is being used effectively and meeting the needs of the organization.
How to avoid enterprise technology buyers remorse

The modern enterprise technology customer has changed significantly over the years.
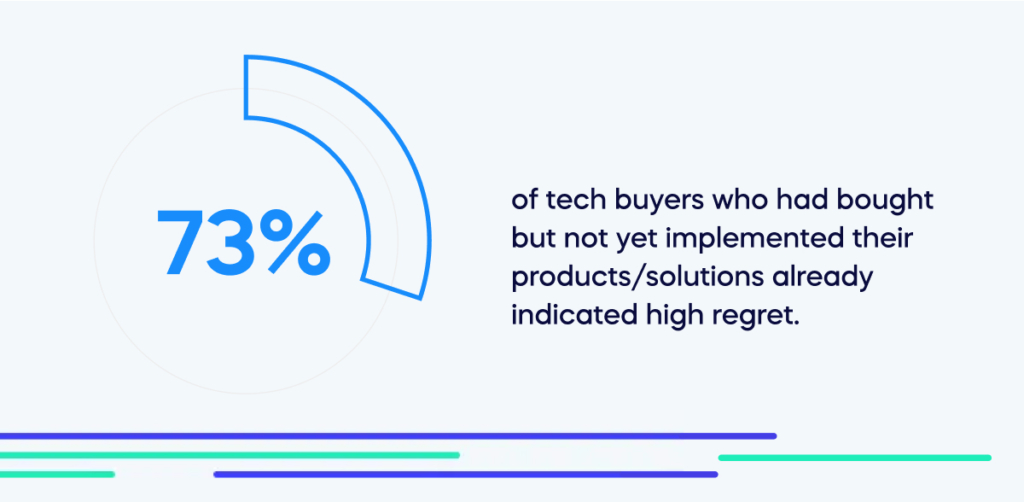
They are more tech-savvy, have access to more options and information than ever, and have numerous opportunities and use cases for tech. However, despite this, many customers often regret their purchase. In fact 73% of tech buyers who had bought but not yet implemented their products/solutions already indicated high regret.
To better understand the causes of high regret, Gartner conducted a study in 2022. They asked tech buyers to indicate to what extent they agreed with two specific statements:
- “The offering we ultimately purchased is failing (or failed) to meet our expectations.”
- “We initially considered offerings that were much more ambitious than what we ultimately decided upon.”
A survey of over a thousand enterprise-tech purchasers revealed that buyers who experience high levels of regret tend to:
Lack of Focus and Clarity in Their Buying Approach
In most cases where buyers experience high regret, conflicting objectives are often at play. This typically arises when these buyers aren’t entirely clear on their evaluation criteria and haven’t defined specific project outcomes or goals.
As a result, they’re more prone to frequently adjusting their project objectives and allowing occasional decision-makers to sway their decisions, leading to increased regret post-purchase.
Have Prolonged Purchasing Cycles
Enter that experience a high level of regret concerning a significant technology purchase decision tend to take longer to complete their purchasing process. On average, this timeframe is approximately seven to 10 months longer than those without regret.
This delay can be attributed to several factors, including the need for additional time to evaluate different options thoroughly, conduct a more rigorous analysis to avoid making similar mistakes, and seek more information to make an informed choice.
Are More Likely to Make No Decision at All
Vendors invest significant resources into attracting potential buyers, but some end up canceling their purchasing efforts or making no decision. This can be due to factors such as budget constraints or unrealistic expectations. Vendors must analyze the reasons behind these cancellations to improve their sales strategies and attract more committed customers.
Adjusting messaging and pricing and providing transparent information about the product or service can help build trust and confidence in the buyer’s decision-making process. By being proactive and adaptable, vendors can tailor their efforts to increase the likelihood of successful conversions and build long-term relationships.
Low-Regret Buyers
Low-regret buyers tend to focus more on achieving specific and gaining internal buy-in. They prioritize clearly defined topics and goals, allowing them to identify the best vendor to help them achieve those objectives.
By quickly deciding and working with a trusted vendor, low-regret buyers can avoid the pitfalls of a prolonged purchasing process. This approach results in greater efficiency, faster implementation of new technology or services, and ultimately, more favorable outcomes.
Enterprise technology buying: A strategic approach for success
Enterprise technology buying is a critical process that can significantly impact an organization’s performance and competitiveness.
Selecting the right technology requires a thorough understanding of the organization’s needs and objectives and the available solutions in the market. The 7-step approach broken down by us and recommended by Gartner provides a comprehensive framework for evaluating and selecting enterprise technologies that meet the organization’s requirements. Each step in the process involves careful planning, evaluation, and collaboration with stakeholders to ensure the technology aligns with the organization’s goals and strategies.
Remember to involve all stakeholders in the decision-making process to ensure that everyone has input into the technology selection. Organizations should also regularly review their technology solutions to identify areas for improvement and ensure that they remain aligned with the organization’s needs.

With careful planning and execution, enterprise technology buying can help organizations achieve their objectives and drive prolonged growth and success.


